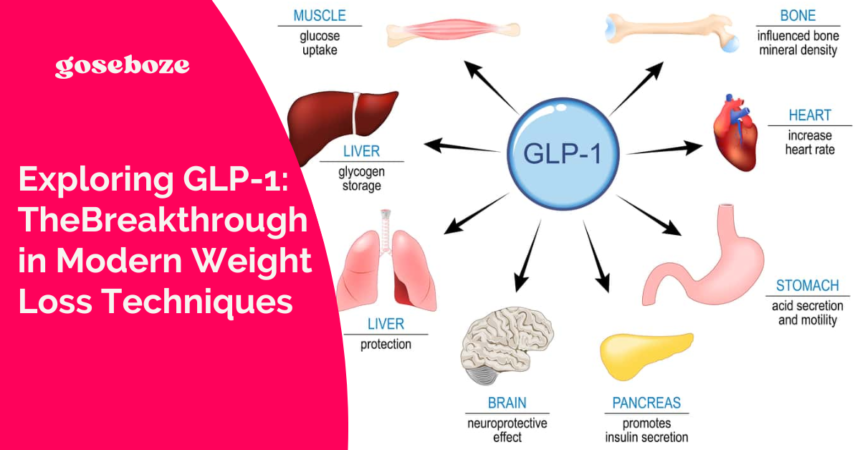
GLP-1, short for Glucagon-like Peptide-1, is a hormone produced naturally in the intestines. It regulates blood sugar levels effectively. Additionally, it plays an essential role in managing appetite. This hormone has become increasingly significant in medical studies.
In recent years, the potential of this hormone in managing obesity has been a focus. Obesity is a significant global health challenge. The role of GLP-1 in this context is critical. The effectiveness of glp 1 for weight loss continues to gain attention.
How This Hormone Affects the Body
Upon food ingestion, GLP-1 is secreted and works by enhancing the release of insulin from the pancreas, which helps lower blood glucose levels. Furthermore, it slows gastric emptying—the rate at which food exits the stomach and goes through the small intestine. This process allows individuals to feel fuller longer, reducing overall caloric intake.
Another crucial function is its ability to decrease glucagon secretion. Glucagon, a hormone that works opposite to insulin, increases blood glucose levels by promoting glucose production in the liver. By inhibiting glucagon, GLP-1 helps further stabilize blood sugar levels, an essential factor in weight management.
GLP-1 Agonists: A New Era in Weight Loss Treatment
Recognizing the benefits of regulating appetite and blood sugar, researchers have developed agonists—medications that mimic the effects of the natural hormone. These agonists bind to the same receptors and have been accepted for use in treating type 2 diabetes and, more recently, for fat loss in adults with obesity.
Effectiveness of Agonists in Clinical Trials
Clinical trials have demonstrated significant results with these agonists. Participants of these medications reported reduced appetite, leading to decreased caloric intake and substantial weight loss over time. Furthermore, these trials highlight improvements in cardiovascular health markers, such as declined blood pressure and improved cholesterol levels.
Safety and Considerations
While these agonists offer promising results, they are only suitable for some. Possible side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects are usually mild to moderate and tend to decline over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
Individuals considering these treatments for weight loss should consult healthcare professionals. A thorough medical evaluation, considering personal health history and any potential drug interactions, can determine the suitability of these treatments.
Lifestyle Factors in Conjunction with Agonists
These agonists should be used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications for optimal results. A balanced diet rich in nutrients and regular physical activity can enhance the effectiveness of based therapies. Healthcare providers often recommend a comprehensive weight loss plan that includes dietary advice, exercise routines, and regular monitoring of health parameters.
Read Also: QXEFV: Advancing Technology with Cutting-Edge Applications 2024
The Future of Hormone-Based Weight Loss
As research continues, the future looks promising. Innovations in drug delivery and new formulations are underway to improve the efficacy and reduce side effects associated with these treatments. Additionally, ongoing studies aim to understand better the full potential of agonists in various populations, including those with conditions beyond type 2 diabetes.
GLP-1 and its agonists represent a significant breakthrough in the fight against obesity. By mimicking the natural actions of the hormone, these medications offer a novel approach to fat loss that goes past traditional diet and exercise. As more individuals turn to these advanced therapies, including glp 1, for weight loss, it is vital to approach weight loss with a well-rounded perspective, incorporating medical guidance, healthy lifestyle choices, and appropriate treatment options. The journey to a healthier weight is complex and individualized, but it is an achievable goal with the right tools and support.